![Vitamin B Complex Benefits]()
Dietary Reference Intake (DRI)
Recommended Dietary Allowance
Does a B-Vitamin Complex really help reduce Stress?
Is it possible to overdose on Vitamin C?
In addition to low Vitamin C and/or Vitamin B1, low tin is a common nutritional cause of low adrenals, which can lead to left-sided cardiac insufficiency.
![Copper Pills]() DRI / RDA Copper and Chromium DRI / RDA Copper and Chromium
|
What is Cellular Nutrition?
Dietary requirements of minerals and their levels are nearly impossible to establish using routine blood tests. Most electrolytes (calcium, magnesium, potassium...) are subject to close homeostatic regulation regardless of dietary intake, while the accuracy of their measurements is compromised by collection, transport, hemolysis, storage, mineral ratios, or processing used. Similar errors are encountered when trying to establish nutritional requirements through serum or plasma panels for zinc, manganese, phosphorus, chromium, selenium, copper, and most other trace elements.
![Intracellular Calcium Measurement with microelectrodes]()
![Intracellular Calcium Measurement with microfluorometry]()
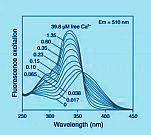
Intracellular Calcium Measurement in neurons with calcium-selective microelectrodes, and microfluorometry.
While an antioxidant-rich diet may provide adequate cellular nutrition for the average, healthy individual - it would be inadequate for those suffering from nutrition related chronic diseases, which require the use of more sophisticated resources that are capable of measuring and optimizing an individual's cellular nutrition status.
|
Myth: If one has a healthy diet, one does not need any supplementation.
Fact: If a large group of people were to follow the exact same dietary lifestyle and exercise program, a certain number would still suffer from high or low blood pressure, high or low blood sugar, or high or low stomach acid, while the rest may develop arthritis, cardiovascular disease, cancer, mental illness, or other medical conditions... Read More
|
Myth: One may liberally supplement mega-doses of water-soluble vitamins since they - unlike fat-soluble vitamins are not stored in the body, so they cannot cause any harm.
Fact: Despite being water-soluble, Vitamin B6 can cause permanent, irreversible nerve damage when used improperly, while an excessive intake or overdose of Vitamin C has the potential of eventually causing zinc, copper, or calcium deficiencies in prone individuals... Read More
|
|



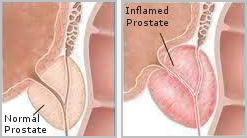 Prostatitis - Offers a clinical perspective of why zinc should not be used in the treatment of this condition.
Prostatitis - Offers a clinical perspective of why zinc should not be used in the treatment of this condition. Mineral Ratios - offers a clinical perspective on the importance of maintaining a proper mineral ratio between calcium, magnesium and other elements.
Mineral Ratios - offers a clinical perspective on the importance of maintaining a proper mineral ratio between calcium, magnesium and other elements. Cancer - Discusses radiation, chemotherapy and anti-cancer drug therapies, and describes some nutritional causes and a possible low stomach acid risk association.
Cancer - Discusses radiation, chemotherapy and anti-cancer drug therapies, and describes some nutritional causes and a possible low stomach acid risk association. Migraine Headaches - Takes an in depth look at how common nutrients can both aggravate and ameliorate headaches, and offers some treatment options.
Migraine Headaches - Takes an in depth look at how common nutrients can both aggravate and ameliorate headaches, and offers some treatment options. Chocolate - Takes a critical look at the recent "Chocolate-is-Good-for-You" campaigns, and dispels some of the health benefit myths.
Chocolate - Takes a critical look at the recent "Chocolate-is-Good-for-You" campaigns, and dispels some of the health benefit myths.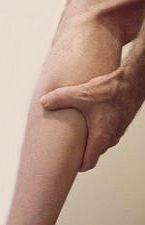 Muscle Spasms and Cramps - Discusses various nutritional causes and treatments for this condition.
Muscle Spasms and Cramps - Discusses various nutritional causes and treatments for this condition. Manganese may help with some symptoms of Parkinson's disease such as muscle rigidity and twitching...
Manganese may help with some symptoms of Parkinson's disease such as muscle rigidity and twitching...
 Research shows that phytosterols such as beta-sitosterol may help normalize the function of natural killer cells and T-helper lymphocytes...
Research shows that phytosterols such as beta-sitosterol may help normalize the function of natural killer cells and T-helper lymphocytes...
 Iron deficiency may be suspect with some forms of ADHD. 84% of children with ADHD were found to have abnormally low levels of ferritin...
Iron deficiency may be suspect with some forms of ADHD. 84% of children with ADHD were found to have abnormally low levels of ferritin...
 A high intake of B Vitamins can trigger heart palpitations, HBP, major complications in patients with congestive heart disease...
A high intake of B Vitamins can trigger heart palpitations, HBP, major complications in patients with congestive heart disease...